|
Core UMTS Network
Elements
The following section sets
out the elements of the GSM/UMTS core network, and some of the reasoning
behind it. Figure 36 shows how these core elements fit together and how
they fit into the overall system picture. However Figure 36 is not a
true physical representation of the core network, nor does it show all
the interfaces. As the core network has not been standardized there
still exist other possibilities for bundling different functions into
physical network elements.
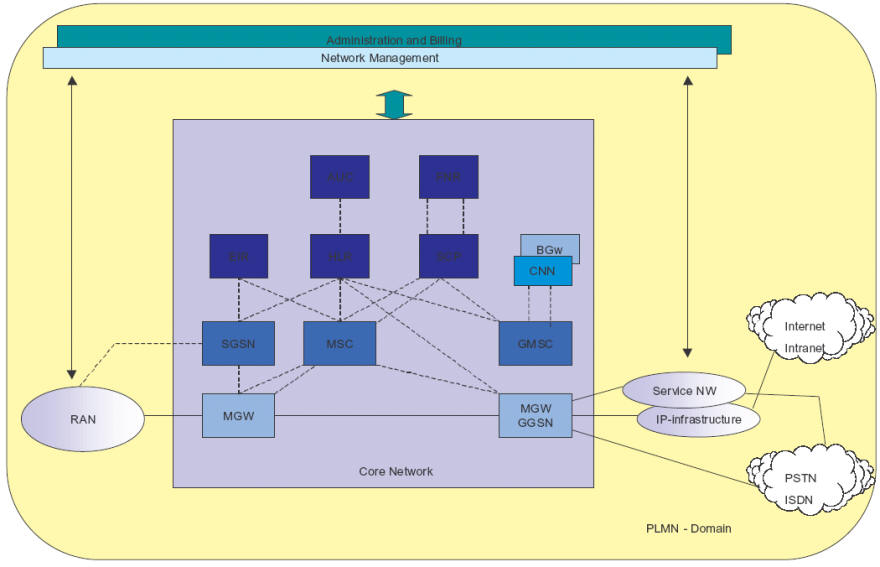
Figure 36 UMTS Core
Network Elements
(Adapted from Ericsson Document EN/LZT 123 5374 R1B)
MSC Server
The MSC Server handles control layer functions related to circuit mode
communication services at the UTRAN and PSTN/ISDN borders and performs
among others the following functions:
-
Media gateway control
-
ISDN services control
-
Mobility management
-
Authentication
-
Charging data
collection/output
-
Services switching
function (5SF)
-
Internet dial-in
services (RAS)
-
Element management
In addition to these
functions the MSC Server also houses the interworking and gateway
functionality necessary to act as an SMS-IWMSC and SMS-GMSC for the
Short Message Service.
Serving GPRS Support
Node Server (SGSN Server)
The SGSN Server handles control layer functions related to packet
mode communication services at the border between UTRAN and the basic
core network and performs among others the following functions:
-
Media gateway control
-
Session management
-
Mobility management
-
Authentication
-
Charging control
-
Relaying of SMS
-
Element management
Media Gateway (MGW)
The MGW handles transport and user plane functions for both packet
and circuit mode communication at the borders between networks/network
segments. These lower layer functions primarily concern the user data
handling and includes e.g.:
-
Media processing
(speech coding. conference call bridging etc)
-
Media generation
(tones etc)
-
Setup/release of user
data bearers
-
Provision of
traffic/charging info for packet mode communication
-
Security management
-
Routing and switching
QoS management
-
Element management
Most MGW resources are
shared between packet and circuit communication services or can easily
be re-configured from one communication mode to the other. This offers a
very cost efficient and flexible solution for managing future changes in
the circuit and packet mode traffic balance.
Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN)
The GGSN constitutes the tunnel end-point for the GPRS specific GTP-tunnel
for packet mode communication and is situated on the border between the
basic UMTS core network and the ISP-POP”. The GGSN is (indirectly)
selected by the end-user at setup of the PDP-context. From an addressing
point of view the GGSN represents the point of presence for ‘logged on’
end-users, i.e. end-users with an established PDP-context. Addresses can
be dynamically assigned (fetched from an external server or a pool of
own addresses) or statically assigned (fetched from the HLR). In order
to fulfill its role in the network the GGSN performs the following
functions among others:
Optionally, a GGSN may
also include certain non-GPRS specific functions such as a Foreign Agent
(FA).
Home Location Register
(HLR)
The Home Location Register is a network database for mobile
telecommunications. The HLR holds all mobile specific subscriber data
and contains a number of functions for managing these data, controlling
services and enabling subscribers to access and receive their services
when roaming within and outside their home PLMN. The HLR communicates
with the GSNs, MSCs and
other network element via the MAP-protocol.
The Authentication
Centre (AUC)
The Authentication Centre (AUC) contains functions for secure storage of
individual subscriber identifiers and keys. AUC also includes algorithms
necessary for generating authentication and ciphering data based on the
subscriber keys. The authentication and ciphering data, provided by the
AUC upon request, are used by different network elements to protect the
network, users and operators against unauthorized use of the system.
Service Control Point (SCP)
The SCP is a part of the IN concept and contains the service logic and
its execution environment. The SCP works in close co-operation with the
service switching functions in the MSCs and provides IN-services such as
Virtual Private Network (VPN), Number Portability etc.
Flexible Number
Register (FNR)
The FNR accommodates translation functions necessary to de-couple
end-user identities from the actual network databases holding end-user
data. These translation functions are essential in order to be able to
e.g.:
Easily reconfigure some of the network databases, e.g. as a result of a
growing number of end-users.
Allow end-users to keep their identities when changing from one
administration to another.
Equipment Identity
Register (EIR)
The Equipment Identity Register is a network database holding status
information on mobile station equipment. The EIR is interrogated by
means of the MAPprotocol from e.g. network elements providing access
into the PLMN (MSC and
SGSN servers), in order to ensure that the mobile station equipment is
not blacklisted for any reason.
Cost Control Node (CCN)
The Cost Control Node is a central part of the 3G charging
environment. CCN contains centralized rating functions and constitutes
the charging determination point for services provided to subscribers at
both into and inter PLMN roaming.
CCN also handles credit limits for accumulated subscriber charges. These
on-line charging mechanism are used for provision of features such as
credit control (e.g. pre-paid), user cost information (advice of
charge), fraud control etc.
CCN receives traffic information on-line and off-line from the different
traffic handling/service nodes and instructs these nodes to proceed with
the calls/services according to the outcome of the operator defined cost
control analyses. CCN also has the ability to receive CDR’s deriving
from the Serving network providing near-real-time revenue charging.
Billing Gateway (BGw)
The Billing Gateway is a key component for the off-line (CDR based)
charging in UMTS. The BGw collects information from the different
traffic handling/service nodes (GSN, MSC. SMS-C. voice mail, application
servers. etc) and forwards it to the operator’s administrative systems
for off-line billing, accounting. traffic analyses and similar
functions. The BGw also acts as an intermediate storage and
pre-processor for formatting the CDR-information into the specific
formats used by the operator.
The BGw also provides an interface to CCN and can be used to relay
information for online charging from the traffic handling/service nodes
not having direct interfaces to CCN.
BGw also acts as an
accounting/settlement broker by providing the ability to distribute
CDR’s from the Serving network to the Home environment BGw or CCN in
near real time.
|

