|
Cell Selection and
Reselection
Comparing GPRS with
circuit switched
In a GSM network the BSC governs the cell selection behavior of the MS
when in idle and active mode by different methods. Idle mode MSs
autonomously performs cell reselection by using the C1/C2 criteria.
In active mode, non-GPRS MSs are steered by the locating functionality
implemented in the BSC. So this means that the BSC initiates the
handovers to other cells. With GPRS, the MS determines the base station
with which it will communicate, Figure 28 shows the handover procedures
for both Circuit Switched and Packet Switched. The GPRS MS manages both
the idle packet and transfer packet mode behaviors.
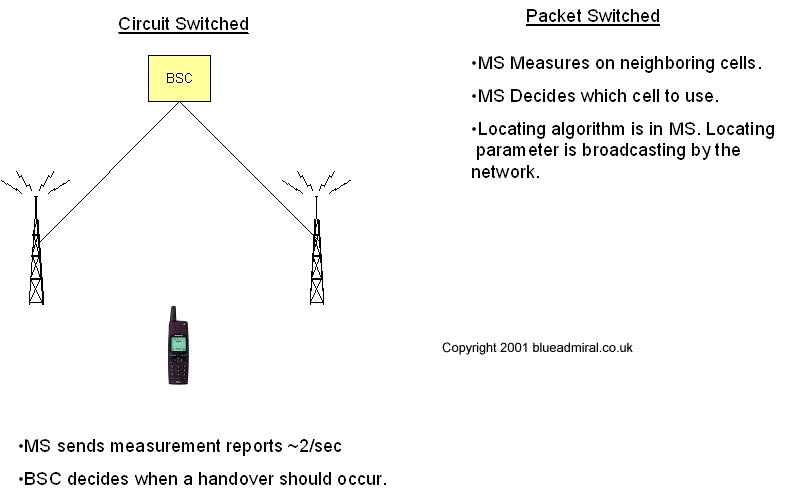
Figure 28 Handover,
comparison between CS and PS
The cell selection and reselection algorithm used for controlling the
idle/transfer mode behaviors are governed by the GPRS cell selection and
reselection parameter setting broadcast in the packet system information
on the PBCCH in each GPRS capable cell with an allocated PBCCH (MPDCH).
If no PBCCH has been allocated in a cell, the GPRS MS will read the
system information broadcast on BCCH and use the C1/C2 criteria for cell
selection and reselection as in the circuit switched idle mode case.
So as you can see the
GPRS cell selection and reselection algorithms are governed by parameter
settings. These parameters C31 and C32 are different to the
corresponding parameters for the circuit switched system. However with
some GPRS systems GPRS cell section parameters are automatically mapped
on those for cell selection/locating known from the circuit switched
case. The reason for this is to achieve the same cell selection behavior
for GPRS, as with GSM, this will enable an easy rollout of GPRS in the
network.
The GPRS standard allow the network to take over cell reselection for a
specific MS or for all MSs. This is called Network Controlled Cell
Reselection and have not yet been implemented in any UK or European GPRS
systems.
|

